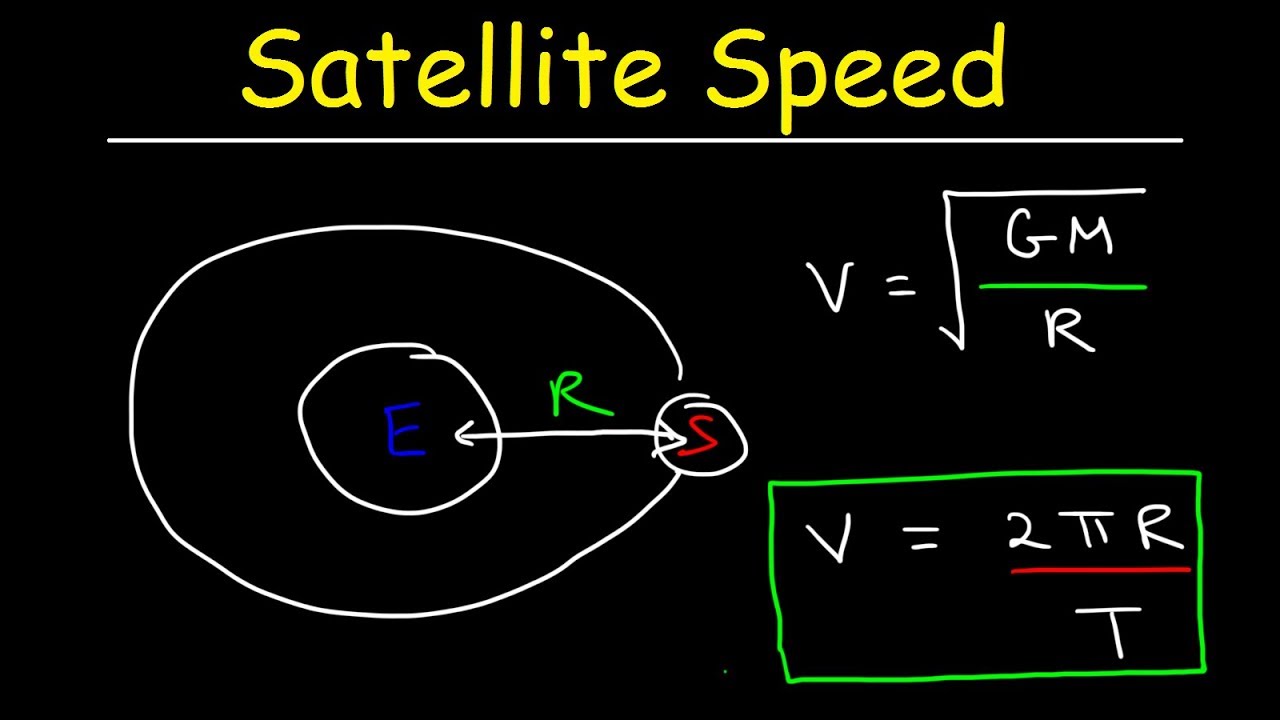
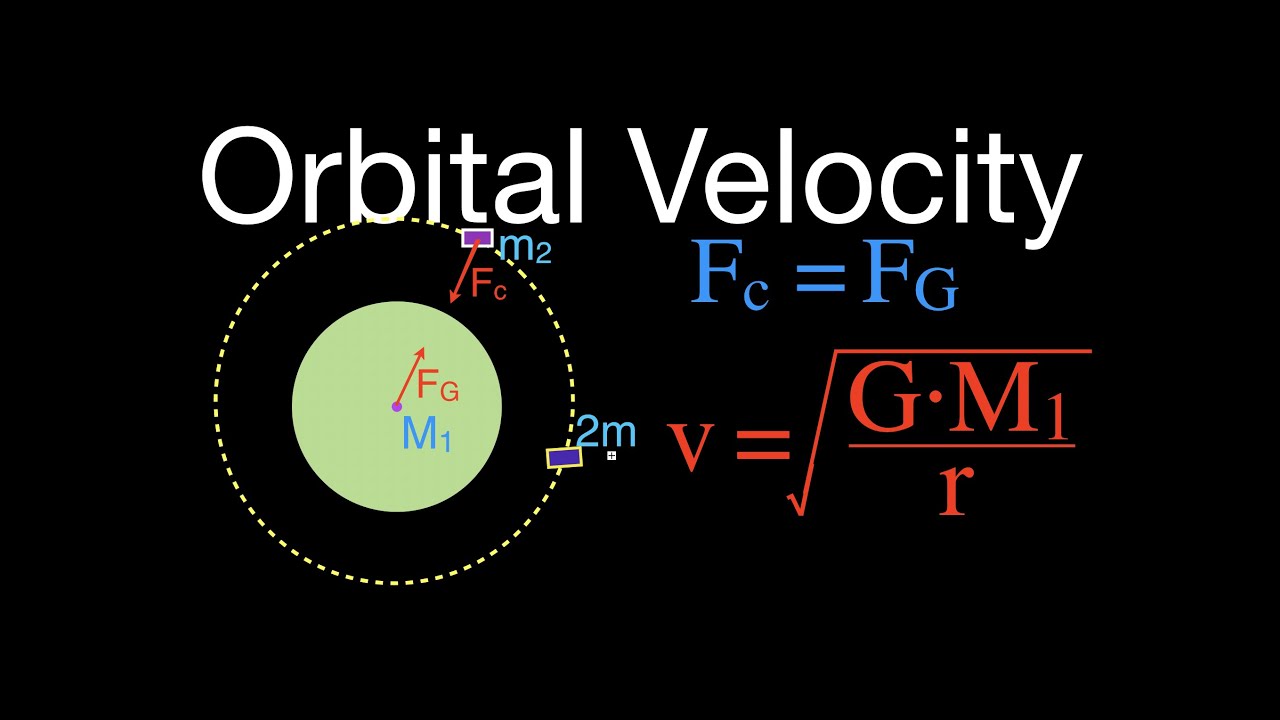
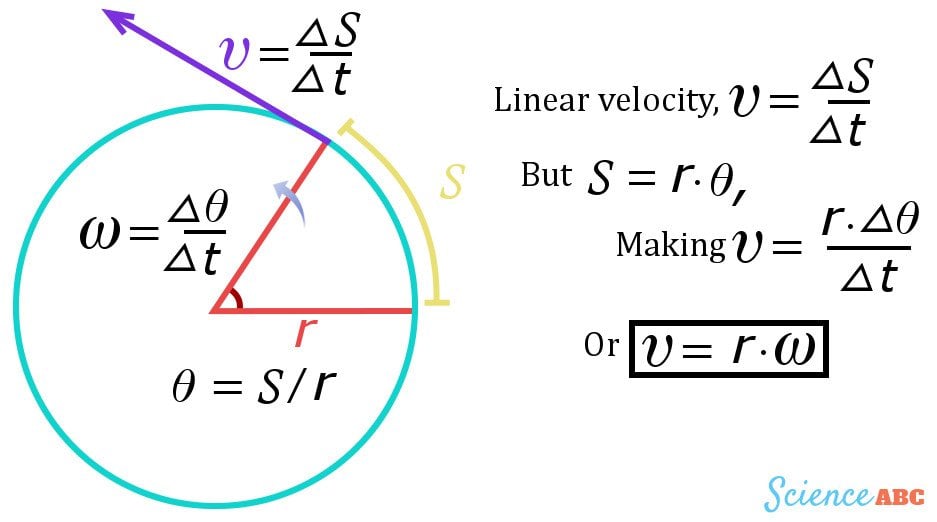Taking the square root of each side leaves the following equation for the velocity of a satellite moving about a central body in circular motion.
Linear velocity of a satellite in a circular orbit is.
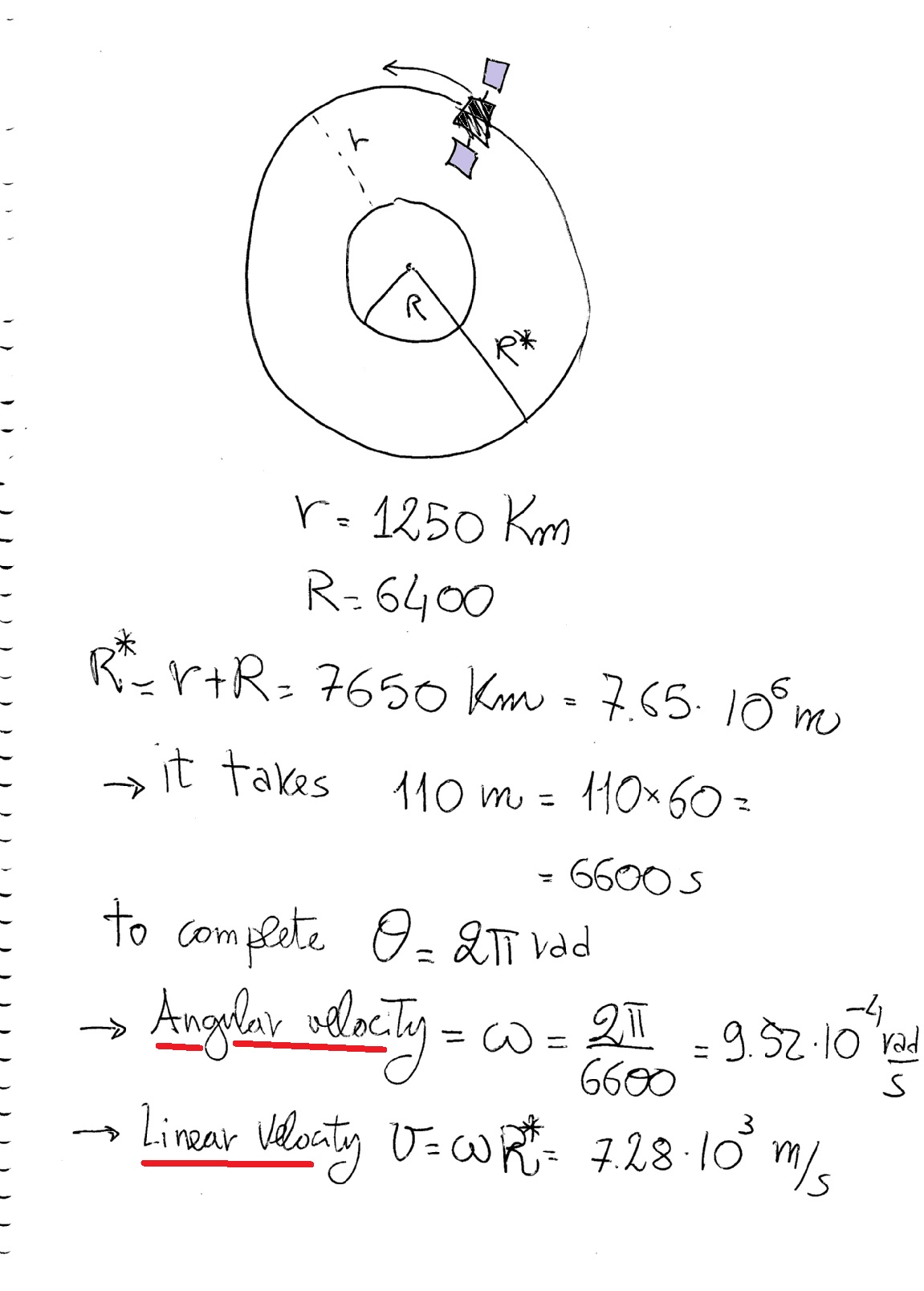
A satellite traveling in a circular orbit 8000km from the earth s center takes 2 hours to make an orbit.
I have a problem from a sample final i believe they have incorrect answers.
In gravitationally bound systems the orbital speed of an astronomical body or object e g.
Below the characteristics of a small satellite orbiting a massive planet at uniform speed in perfectly circular orbit are derived.
Now this r is the sum of the radius of the earth r and the height h of the satellite from the surface of the earth.
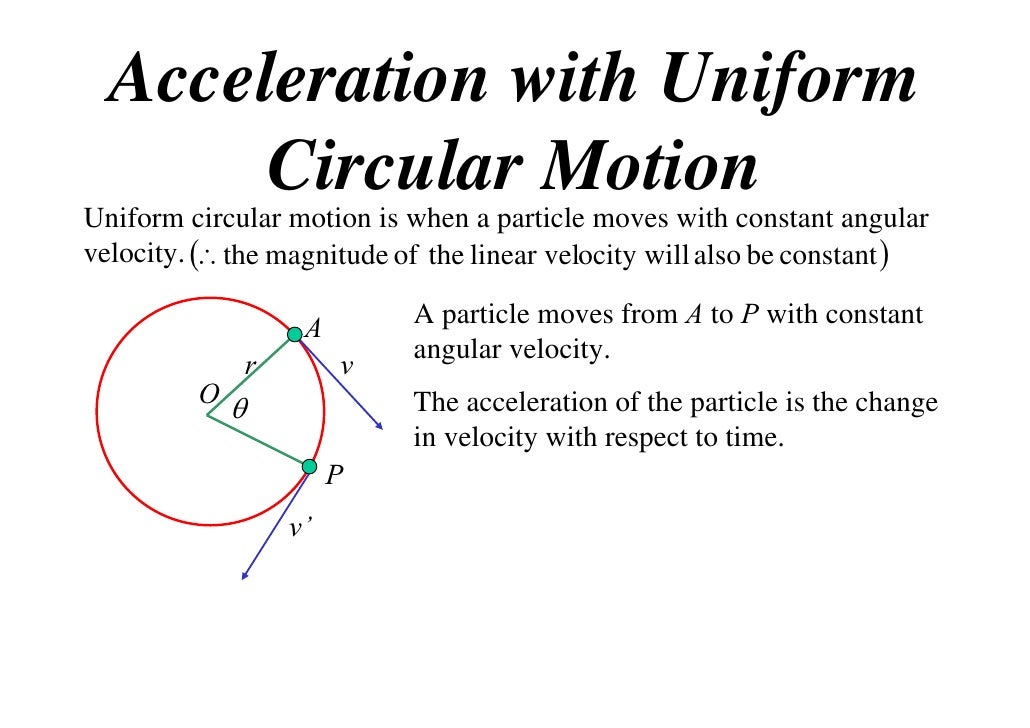
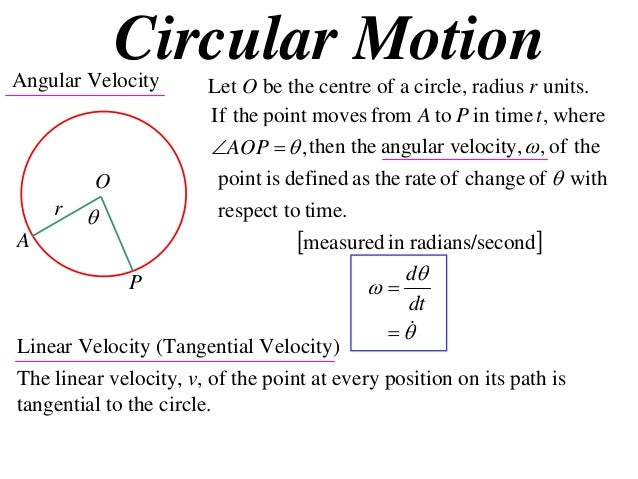
What is the linear velocity of the satellite and what is the angular velocity of the satellite.
A circular orbit is the orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter that is in the shape of a circle.
Here m is the mass of earth and m is the mass of the satellite which is having a uniform circular motion in a circular track of radius r around the earth.
This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the speed of a satellite in circular orbit and how to calculate its period around the earth as well.
V is the linear velocity of the satellite at a point on its circular track.
R 3 897 x 10 7 m the orbital radius for this satellite is 3 897 x 10 7 m.
What is the orbital radius.
The orbital radius can be found by rearranging the orbital velocity formula.
However when a small object like a satellite asteroid or small moon orbits a large object like a planet or star it is a good approximation to treat the system as a two body system with the larger body fixed.
The term can be used to refer to either.
Where g is 6 673 x 10 11 n m 2 kg 2 m central is the mass of the central body about which the satellite orbits and r is the radius of orbit for the satellite.
Here the centripetal force is the gravitational force and the axis mentioned above is the line through the center of the central mass perpendicular to the plane of motion.
2 a satellite is orbiting the earth with an orbital velocity of 3200 m s.
Listed below is a circular orbit in astrodynamics or celestial mechanics under standard assumptions.